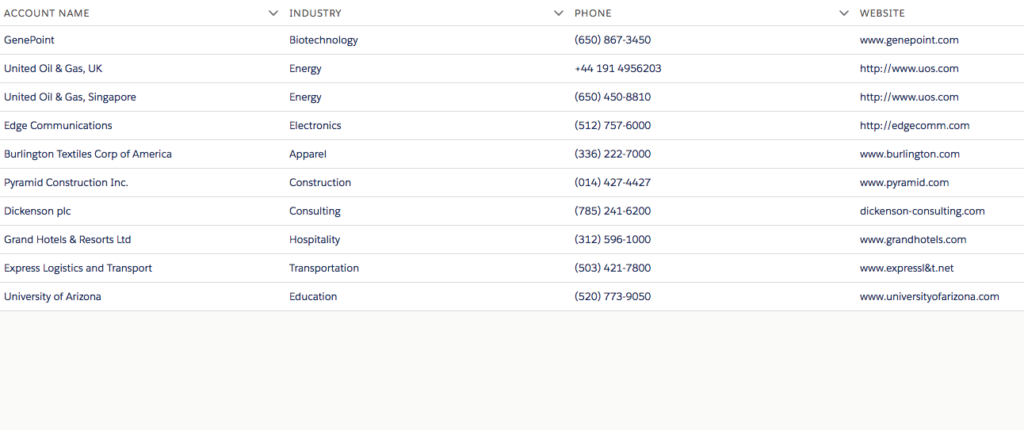
Modal/Popup Lightning Component Salesforce
Modal/Popup Lightning Component Salesforce
In this post, We will simply create a custom Lightning Modal/Popup Box in the salesforce lightning component.
What is Modal in Salesforce Lightning Experience ?
Modals/Popup Box are used to display content in a layer above the app. This paradigm is used in cases such as the creation or editing of a record, as well as various types of messaging and wizards.
Modal/Popup Lightning Component Salesforce looks like following image
ModalPopupExample1 Lightning Component
In this code we are first declaring ‘isModalOpen’ attribute and setting its default value as false. Then using aura:if we are conditionally displaying modal/popup on click of button. For more details about aura:if, please refer my previous post aura:if in lightning component example
Also code has following three main part
- section
- header
- footer
Details are explained in code comment.
Following is expected markup
Expected markup in in modal/popup
- Modal has
role="dialog" - When the modal is open, everything behind it has HTML attribute
aria-hidden="true", so assistive technology won’t read out the underlying page. The best way to do this is to give the modal and the page separate wrapper elements and togglearia-hidden="true"/aria-hidden="false"on the main page’s wrapper depending on whether or not the modal is open. - Modal contains an HTML heading
- Modal has an
aria-labelledbyattribute whose value is the id of the modal’s heading
<aura:component>
<!--Boolean attribute to indicate if modal is open or not
default value is false as modal is closed when page is loaded
-->
<aura:attribute name="isModalOpen" type="boolean" default="false"/>
<div class="slds-m-around_xx-large">
<lightning:button variant="brand"
label="What is Modal/PopUp Box?"
title="What is Modal/PopUp Box?"
onclick="{! c.openModel }" />
<!--Use aura:if tag to display/hide popup based on isModalOpen value-->
<aura:if isTrue="{!v.isModalOpen}">
<!-- Modal/Popup Box starts here-->
<section role="dialog" tabindex="-1" aria-labelledby="modal-heading-01" aria-modal="true" aria-describedby="modal-content-id-1" class="slds-modal slds-fade-in-open">
<div class="slds-modal__container">
<!-- Modal/Popup Box Header Starts here-->
<header class="slds-modal__header">
<lightning:buttonIcon iconName="utility:close"
onclick="{! c.closeModel }"
alternativeText="close"
variant="bare-inverse"
class="slds-modal__close"/>
<h2 id="modal-heading-01" class="slds-text-heading_medium slds-hyphenate">Modal/PopUp Box</h2>
</header>
<!--Modal/Popup Box Body Starts here-->
<div class="slds-modal__content slds-p-around_medium" id="modal-content-id-1">
<p><b>Modals/Popup Box are used to display content in a layer above the app. This paradigm is used in cases such as the creation or editing of a record, as well as various types of messaging and wizards.
</b>
</p>
</div>
<!--Modal/Popup Box Footer Starts here-->
<footer class="slds-modal__footer">
<lightning:button variant="neutral"
label="Cancel"
title="Cancel"
onclick="{! c.closeModel }"/>
<lightning:button variant="brand"
label="OK"
title="OK"
onclick="{!c.submitDetails}"/>
</footer>
</div>
</section>
<div class="slds-backdrop slds-backdrop_open"></div>
</aura:if>
</div>
</aura:component>
Lightning Component Controller
({
openModel: function(component, event, helper) {
// Set isModalOpen attribute to true
component.set("v.isModalOpen", true);
},
closeModel: function(component, event, helper) {
// Set isModalOpen attribute to false
component.set("v.isModalOpen", false);
},
submitDetails: function(component, event, helper) {
// Set isModalOpen attribute to false
//Add your code to call apex method or do some processing
component.set("v.isModalOpen", false);
},
})
Lightning component App ModalPopupExampleApp1
<aura:application extends="force:slds"> <c:ModalPopupExample1/> </aura:application>
More details about lightning modal/popup
Modals always have an equal amount of space at the top and bottom to account for the height of the close button.
Modals grow according to how much content is within, but once the modal reaches full height (including the previously mentioned space on top and bottom), the content area will begin to scroll. (This scrolling is currently not available in Salesforce1 Mobile.)
For more details about modal in lightning, please refer to modal lightning




Happy Coding:)