Page Contents
Git Commands With Examples
Git Commands With Examples
What is git?
Git is a distributed version-control system for tracking changes in source code during software development. It is designed for coordinating work among programmers, but it can be used to track changes in any set of files. Its goals include speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows.
Git is a free, open source distributed version control system tool designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency. It was created by Linus Torvalds in 2005 to develop Linux Kernel. Git has the functionality, performance, security and flexibility that most teams and individual developers need. It also serves as an important distributed version-control DevOps tool.
Features of Git
- Free and open source
- Speed
- Scalable
- Reliable
- Secure
- Economical
- Supports non-linear development
- Easy Branching
- Distributed development
- Compatibility with existing systems or protocol
Git Commands
Here is list of important git commands:
- git config
- git init
- git clone
- git status
- git add
- git commit
- git diff
- git push
- git pull
- git branch
- git checkout
- git stash
- git merge
- git reset
- git remote
Git Cheat Sheet
Here is our cheat sheet for git commands
Git Commands with examples
Let’s dive deep and check more details about each git command
Here is list of important git commands with examples:
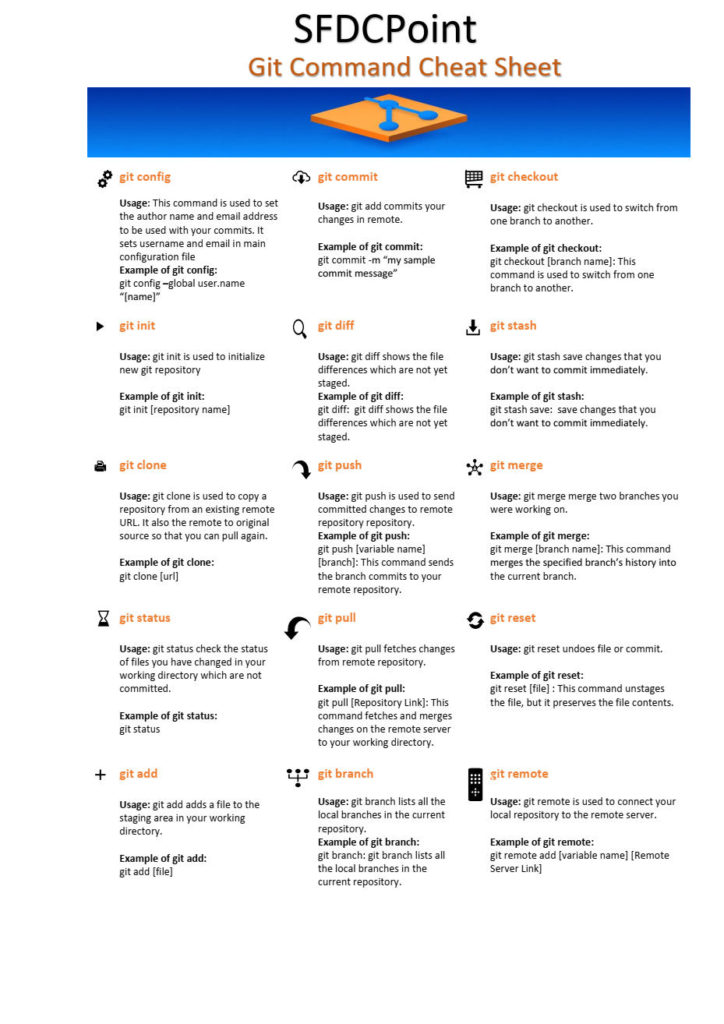
git config
Usage: This command is used to set the author name and email address to be used with your commits. It sets username and email in main configuration file
Example of git config:
git config –global user.name “[name]”
git config –global user.email “[email address]”
git init
Usage: git init is used to initialize new git repository
Example of git init:
git init [repository name]
git clone
Usage: git clone is used to copy a repository from an existing remote URL. It also the remote to original source so that you can pull again.
Example of git clone:
git clone [url]
git status
Usage: git status check the status of files you have changed in your working directory which are not committed.
Example of git status:
git status
git add
Usage: git add adds a file to the staging area in your working directory.
Example of git add:
git add [file]
git add *
git commit
Usage: git add commits your changes in remote.
Example of git commit:
git commit -m “my sample commit message”
git diff
Usage: git diff shows the file differences which are not yet staged.
Example of git diff:
git diff: git diff shows the file differences which are not yet staged.
git diff –staged: This command shows the differences between the files in the staging area and the latest version present.
git push
Usage: git push is used to send committed changes to remote repository repository.
Example of git push:
git push [variable name] [branch]: This command sends the branch commits to your remote repository.
git push –all [variable name]: This command pushes all branches to your remote repository.
git pull
Usage: git pull fetches changes from remote repository.
Example of git pull:
git pull [Repository Link]: This command fetches and merges changes on the remote server to your working directory.
git branch
Usage: git branch lists all the local branches in the current repository.
Example of git branch:
git branch: git branch lists all the local branches in the current repository.
git branch [branch name]: It creates a new branch.
git branch -d [branch name]: It deletes branch with branch name.
git checkout
Usage: git checkout is used to switch from one branch to another.
Example of git checkout:
git checkout [branch name]: This command is used to switch from one branch to another.
git checkout -b [branch name]: This command creates a new branch and also switches to it.
git stash
Usage: git stash save changes that you don’t want to commit immediately.
Example of git stash:
git stash save: save changes that you don’t want to commit immediately.
git stash pop: This command restores the most recently stashed files.
git stash list: This command lists all stashed changes.
git stash drop: This command discards the most recently stashed changes.
git merge
Usage: git merge merge two branches you were working on.
Example of git merge:
git merge [branch name]: This command merges the specified branch’s history into the current branch.
git reset
Usage: git reset undoes file or commit.
Example of git reset:
git reset [file] : This command unstages the file, but it preserves the file contents.
git reset [commit] : This command undoes all the commits after the specified commit and preserves the changes locally.
git reset –hard [commit] : This command discards all history and goes back to the specified commit.
git remote
Usage: git remote is used to connect your local repository to the remote server.
Example of git remote:
git remote add [variable name] [Remote Server Link]
For more details about git please refer this link


Recent Comments